

See the Ports page for more details on their set up. Ports are placed over the input and output traces to inject the transmission-line mode over a frequency range of 0.5 – 1.5 GHz and calculate the devices scattering parameters. The resistor is modeled using a 2D rectangular sheet that is assigned an material with R=100 Ohms. The quarter-wave transmission lines are constructed using 2D polygons formed into an annular shape whose circumference is calculated using Eqs. 3.195 and 3.197 in Pozar (see the microstrip.lms script file in the microstrip example) to be 4.9mm (Z 0=50 Ohms) and 2.804 mm (√2Z 0=70.7 Ω). The required width of each transmission line section is calculated using Eqs.

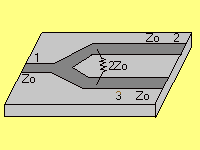
The microstrip transmission lines are modeled using 2D perfect electric conductor (PEC) rectangular sheets placed on top of a 1.59mm thick substrate that possesses a relative permittivity of 2.2. The structure group “traces and load” is used to construct and set the physical and electrical parameters of the Wilkinson power divider in the FDTD simulation file wilkinson_power_divider.fsp. Using FDTD, we will determine the frequency response of the Wilkinson power divider for Example 7.2 in Pozar where f0=1 GHz, Z0=50 Ω, √2Z0=70.7 Ω, and R=2Z0=100 Ω. Using even- and odd-mode transmission-line analysis, the Wilkinson power divider can be shown to possess the following scattering parameters at the design frequency: S11= 0, S12=S13=-j/√2, S23=S32=0. A shunt resistor (R) of value 2Z0 is symmetrically placed between the output branches to achieve high isolation between the output ports. The above figure presents the layout of the Wilkinson power divider which consists of an input transmission line with a characteristic impedance Z0 that branches into two quarter-wavelength transmission-line sections of characteristic impedance √2Z0 that carry power into the output transmission lines of characteristic impedance Z0. FDTD will be used to obtain the scattering parameters of the device. Although the Wilkinson power divider can be designed to achieve arbitrary power division (e.g., see Pozar ), this example will investigate the equal-split (3dB) case. The Wilkinson power divider is a power divider circuit that achieves isolation between its two output ports when all ports are matched.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
